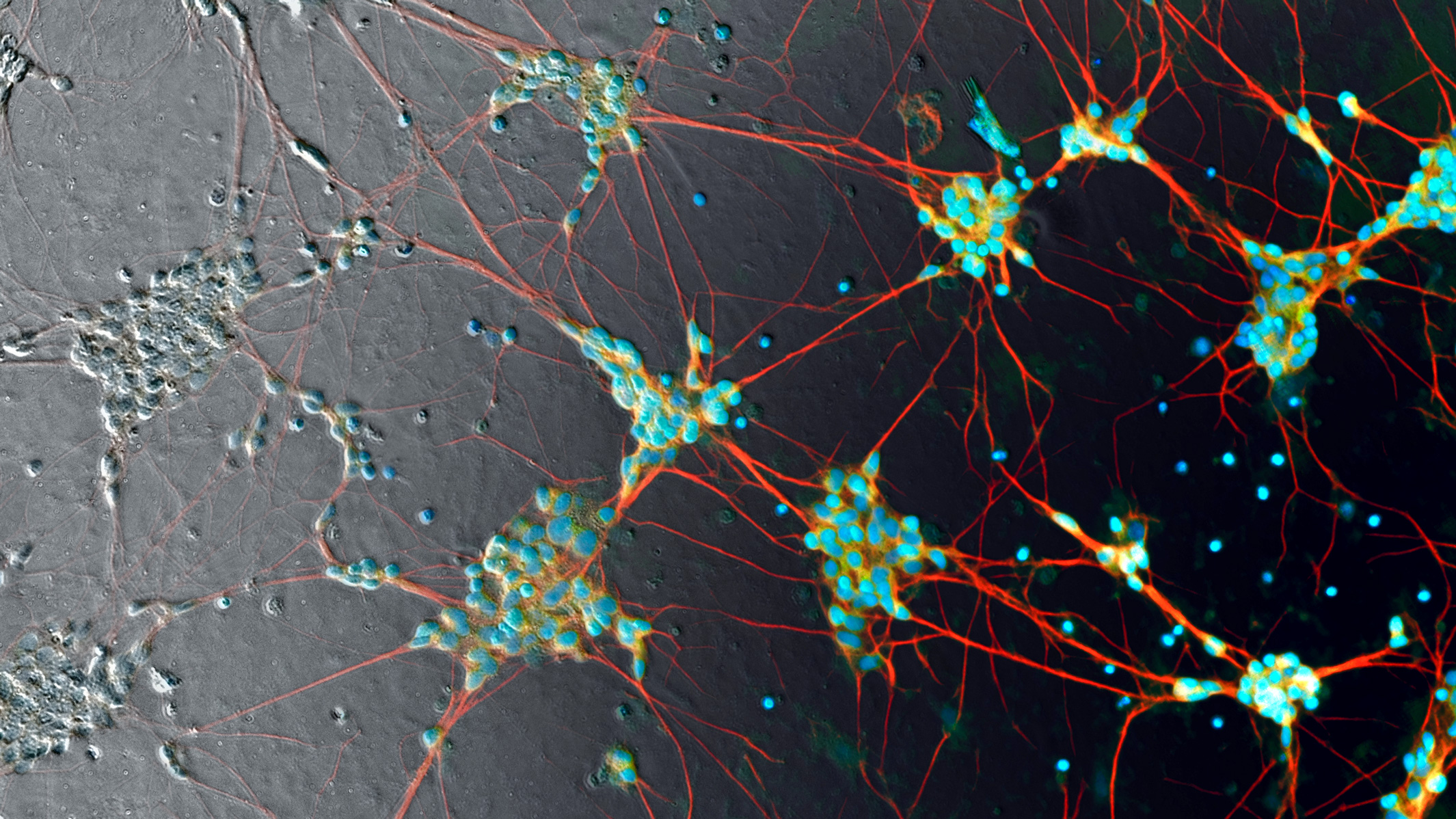
产业进展
2021年11月,Xilis公司获得7000万美元投资,用于开发其实验性癌症治疗技术。2019年,沈西凌、David Hsu和Hans Clevers联合创立Xilis,并开发创立了“微生物圈”(microorgansphere)的技术,简称MOS,它从癌症患者身上提取组织样本,并将其转化为患者癌症肿瘤的数千个微型副本。
成果报道
2022年5月,沈西凌、David Hsu联合Hans Clevers在Cell Stem Cell上发表了文章Patient-derived micro-organospheres enable clinical precision oncology,基于液滴微流控技术利用癌症患者少量组织即可产生大量微小类器官球体(micro-organospheres,MOS),可在14天内完成对药物反应的评估。
2020年12月30日,其在Cell Host & Microbe杂志上文章设计了一种新的数据算法,可以从癌症基因组图谱(TCGA)中删除受污染的微生物遗传信息, 从而首次得到健康和癌变状态下各个器官中生活的微生物群的清晰图片。研究人员现在将能够发现疾病的新生物标记,并更好地了解众多癌症如何影响人体。
2020年4月,沈西凌团队与西安交通大学黄强团队和麻省理工学院Rudolf Jaenisch团队合作在Science杂志上发表研究报告,他们开发了一种小鼠胚胎发育活体成像技术,通过不同发育阶段的“腹窗”,首次实现了高分辨成像观察小鼠胚胎第9.5天至出生的连续发育过程。
科研课题
2021年-2024年,美国国防部,Transcriptional reprogramming of lethal small cell prostate cancer,联合项目
2019年-2024年,美国国防高级研究项目局,Mapping Epigenetic Memory of Exposure New To Observe (MEMENTO),首席研究员
2020年-2023年,美国Hartwell基金会,Developing bacteria-derived therapies to cure inflammatory bowel diseases,联合项目
2019年-2023年,美国国防部,Effects of storage method on intestinal allograft immune profile and viability,调研项目
2019年-2023年,美国NIH,Developing a comprehensive model for peripheral nerve stimulation of gastrointestinal function,首席研究员
人物简介
沈西凌,博士,Xilis公司联合创始人,美国杜克大学病理学兼职教授,上海人,在斯坦福大学获得本硕、博士学位(2008年),曾在加州大学伯克利分校从事博士后研究。The Shen lab uses systems biology to study spatiotemporal controls of multicellular systems, and how their subversion lead to diseases. Ongoing projects include colon cancer, normal and cancer stem cells, non-coding RNA, enteric nervious system, and tuberculosis.
任职情况
2023年至今,美国杜克大学病理学兼职教授
2015年-2021年期间担任:
美国杜克大学肿瘤研究所生物医学工程学院的副教授
Associate Professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering
Hawkins Family Associate Professor
Associate Professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Associate Professor in Molecular Genetics and Microbiology
Member of the Duke Cancer Institute
Affiliate of the Regeneration Next Initiative
联众医疗生物工程首席科学家
教育背景
Ph.D. Stanford University, 2008
M.Sc. Stanford University, 2001
B.Sc. Stanford University, 2001
讲授课程
BME 260L: Modeling Cellular and Molecular Systems
BME 493: Projects in Biomedical Engineering (GE)
BME 590L: Special Topics with Lab
EGR 393: Research Projects in Engineering
学术文章(2024年)
Longitudinal intravital imaging of mouse placenta,PMID: 38507481 PMCID: PMC10954206 DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adk1278
Tissue-resident memory T cell signatures from single-cell analysis associated with better melanoma prognosis,PMID: 38455971 PMCID: PMC10918229 DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109277
Patient-Derived Organoids as Therapy Screening Platforms in Cancer Patients,PMID: 38359321 DOI: 10.1002/adhm.202302331
Patient-Derived Models of Cancer in the NCI PDMC Consortium: Selection, Pitfalls, and Practical Recommendations,PMID: 38339316 PMCID: PMC10854945 DOI: 10.3390/cancers16030565
Activation of cytotoxic lymphocytes through CD6 enhances killing of cancer cells,PMID: 38280067 PMCID: PMC10821976 DOI: 10.1007/s00262-023-03578-1
Epigenetic and transcriptional responses in circulating leukocytes are associated with future decompensation during SARS-CoV-2 infection,PMID: 38179063 PMCID: PMC10765013 DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108288
The KRAS tour: Studying metabolic reprogramming in isogenic pancreatic cancer organoids,PMID: 38181746 DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.12.010
参考阅读
https://scholars.duke.edu/person/xiling.shen
前哨.2018科技特训营《精准医疗和个性化医疗》口述
http://shenlab.pratt.duke.edu/people/xiling-shen?
https://fitzpatrick.duke.edu/faculty/xiling-shen
https://xilis.com/
领英账号:https://www.linkedin.com/in/xiling-shen-75816b2/